Services
Understanding The Source Of Pain
We never treat without proper diagnosis, so we take imaging seriously. Imaging is critical in helping your doctor pinpoint the source of your pain, then devise a plan to relieve it quickly and keep it away for as long as possible. You can bring us any imaging you already have, such as MRIs or CT scans. Or we will refer you to our world-class imaging partners.

Interventional Spine Treatments
Non-opioid approach to avoid additional problems down the road.
Diagnostics
Assists in identifying the source of advanced, chronic back pain. Using imaging guidance, a contrast material is injected into the center of one or more spinal discs. As part of the procedure, an x-ray or CT scan also may be performed to obtain pictures of the injected disc. Though more invasive than some other imaging procedures, discography is generally safe.

Examines the soft tissues surrounding the musculoskeletal system to aid in determining the cause of abnormal pain or discomfort. The images give a detailed, 3D look at muscles, tendons, ligaments and blood vessels, allowing diagnosis of even the smallest tears and injuries. Patients lie on a table that slides into the MRI machine’s tube. An MRI is painless and can last from 15 minutes to an hour.

Provides a 3D view of a part of the body, revealing a detailed picture of the anatomy of bones and joints. As with MRI, patients lie comfortably on a table that slides into the machine. The process typically takes around 30 minutes.

Helpful in diagnosing a variety of muscle and nerve disorders. For an EMG test, a tiny needle electrode is inserted directly into a muscle and records the muscle’s electrical activity. Electrode patches applied to the skin during NCS stimulate the nerve with a very mild electrical impulse to calculate how fast that impulse moves through the nerves. These tests can be done separately or the same time.

Used to identify if one or more facet joints may be the source of back pain. The skin is numbed, then a small amount of local anesthetic is injected into a facet joint adjacent to the spine. How much relief the patient experiences – and for how long – assist in determining the treatment path.

Fluoroscopy is an X-ray imaging method that creates a live, moving image of the body’s internal structures and organs in real time used during spinal procedures.
Treatments
Epidural Steroid Injection (ESI)
Clinically proven to be effective in alleviating pain. A small dose of steroid is injected into the epidural space in the cervical, thoracic or lumbar spine. This common procedure takes only 10 to 30 minutes and patients often see pain relief and improved motion within a day or two. Depending on the patient, relief can last for several months.
Nerve Block
A nerve block for a discogram (also called a selective nerve root block or SNRB) is a procedure where a local anesthetic and/or anti-inflammatory medication is injected near a specific nerve root. This helps temporarily block pain signals and can be used to diagnose or treat pain caused by a herniated disc or other spinal conditions.
SI Joint Injections
SI joint injections are a treatment option to help relieve pain and reduce inflammation in the sacroiliac joints. These joints connect the lower part of your spine (sacrum) to the upper part of your pelvis (ilium).
Radio Frequency Ablation (RFA)
Generally providing longer-term pain relief, this procedure involves inserting a small, insulated needle or cannula next to pain-carrying nerves. Local anesthetic numbs the area, then heat is generated and precisely delivered to a small area of tissue, destroying the nerve endings. The procedure itself takes no longer than injections, but pain can be reduced or eliminated for anywhere from a few months to a year.
Discectomy
A discectomy is a procedure done to relieve pain and other symptoms caused by a herniated disc. This happens when the soft, gel-like center of a disc (nucleus pulposus) pushes through its tough outer layer (annulus fibrosus) and presses on nearby nerves.
ION Facet Fusion
The ION Facet Fusion procedure is a minimally invasive spinal fusion technique that uses the ION Facet Screw System to stabilize and fuse the facet joints in the spine. This approach provides a less invasive alternative to traditional spine surgery.
Non Opioid Medications
Creams that include non-narcotic pain relief and/or anti-inflammatory agents can be applied to painful area, including joints. Opioids are never prescribed as part of a patient treatment plan.
Orthopedics
Injury treatment without the recovery time of traditional surgery.

Diagnostics
Treatments
Joint Injections
Joint injections are a common treatment option to help reduce pain and inflammation in joints. They provide a non-surgical solution for conditions like arthritis or joint injuries. Common types of injections include corticosteroid and viscosupplementation injections.
Bracing-DME
Orthopedic bracing is a device designed to support and stabilize an injured or weak joint, muscle, or bone. It’s a non-surgical option that helps protect the area, prevent further injury, and promote faster healing.
PRP
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy allows us to use your own blood to reduce your pain and help you heal from soft tissue injuries, such as ligament and tendon injuries.
Neurology
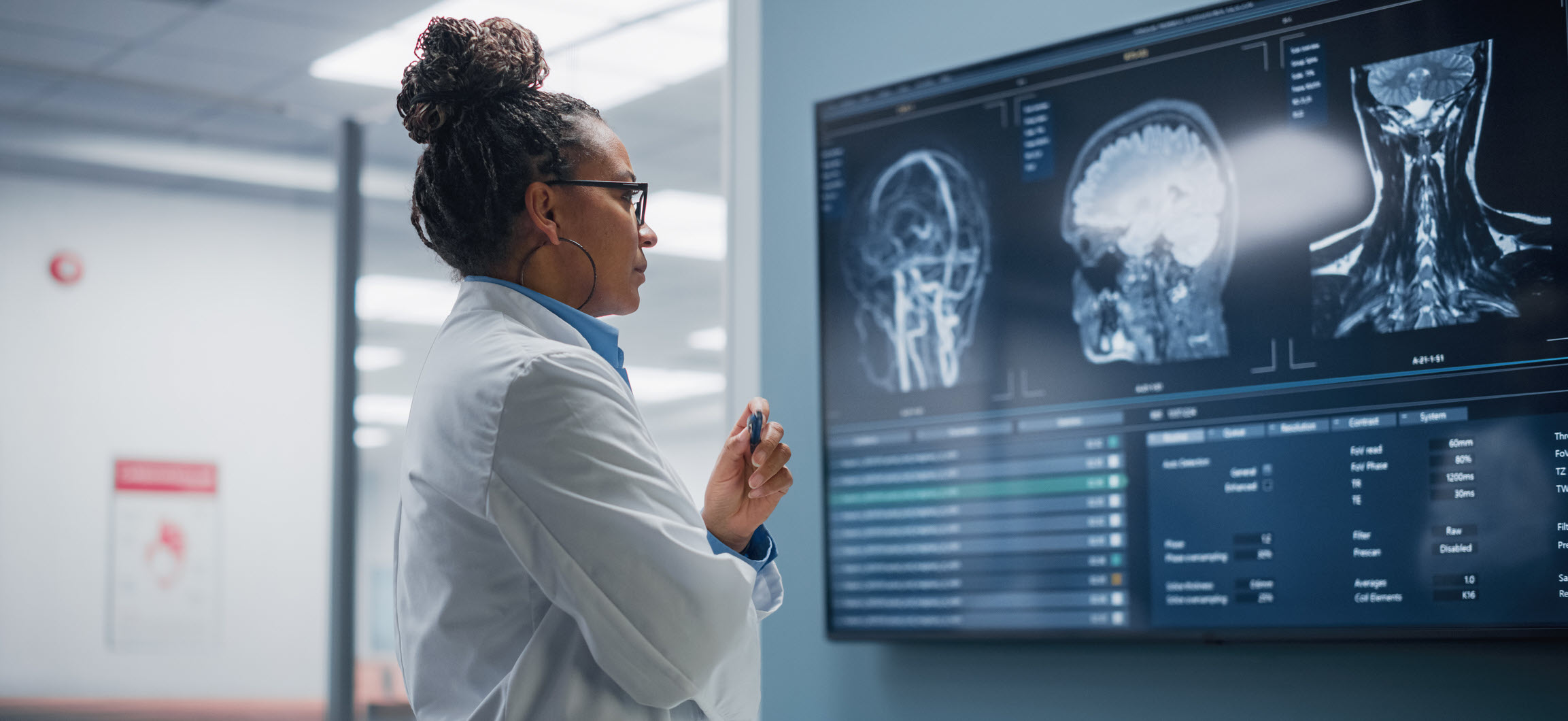
Electromyography (EMG) and Nerve Conduction Studies (NCS)
Helpful in diagnosing a variety of nerve and muscular disorders. For an EMG test, a tiny needle electrode is inserted directly into a muscle and records the muscle’s electrical activity. Electrode patches applied to the skin during NCS stimulate the nerve with a very mild electrical impulse to calculate how fast that impulse moves through the nerves. These tests can be done separately or the same time.Discography
Assists in identifying the source of advanced, chronic back pain. Using imaging guidance, a contrast material is injected into the center of one or more spinal discs. As part of the procedure, an x-ray or CT scan also may be performed to obtain pictures of the injected disc. Though more invasive than some other imaging procedures, discography is generally safe.Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
Examines the soft tissues surrounding the musculoskeletal system to aid in determining the cause of abnormal pain or discomfort. The images give a detailed, 3D look at muscles, tendons, ligaments and blood vessels, allowing diagnosis of even the smallest tears and injuries. Patients lie on a table that slides into the MRI machine’s tube. An MRI is painless and can last from 15 minutes to an hour.Computed Tomography (CT Scan)
Provides a 3D view of a part of the body, revealing a detailed picture of the anatomy of bones and joints. As with MRI, patients lie comfortably on a table that slides into the machine. The process typically takes around 30 minutes.
